进程和线程介绍
- 进程就是程序在操作系统中的一次执行过程,是系统进行资源分配和调度的基本单位。
- 线程是进程中的一个执行实例,是程序执行的最小单元,它是比进程更小的能独立运行的基本单位。
- 一个进程可以创建和销毁多个线程,同一个进程中的多个线程可以并发执行。
- 一个程序至少有一个进程,一个进程至少有一个线程。
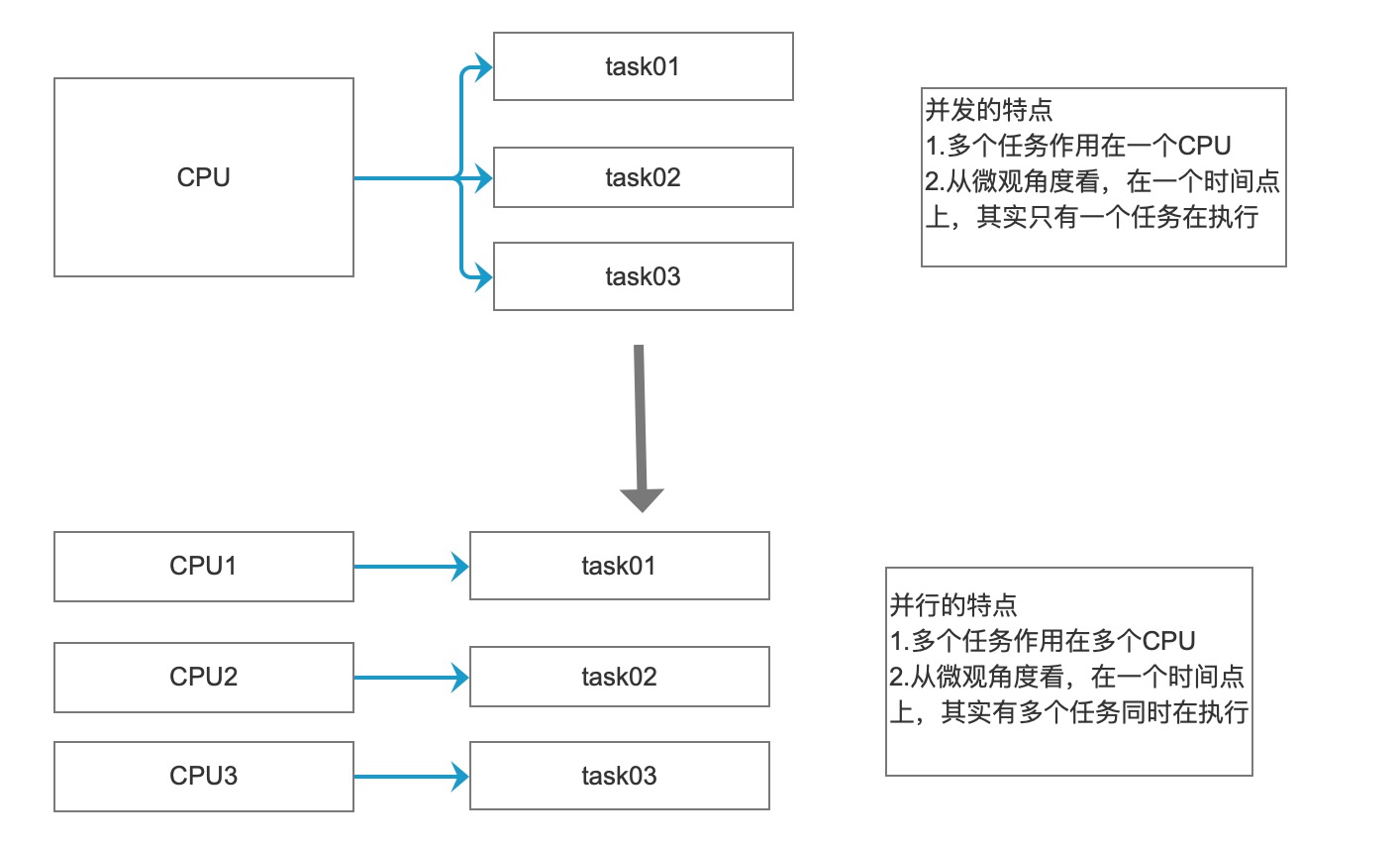
并发和并行
- 多线程程序在单核上运行,就是并发。
因为是在一个CPU上,比如有10个线程,每个线程执行10毫秒(进行轮询操作),从人的角度看,好像这10个线程都在执行,但是从微观上看,在某一个时间点看,其实只有一个线程在执行,这就是并发。 - 多线程程序在多核上运行,就是并行。
因为是在多个CPU上(比如有10个CPU),比如有10个线程,每个线程执行10毫秒(各自在不同的CPU上执行),从人的角度看,这10个线程都在运行,但是从微观上看,在某一个时间点看,也同时有10个线程在执行,这就是并行。
Go 协程和Go 主线程
- Go主线程(有程序员直接成为线程/也可以理解为进程):一个Go线程上,可以起多个协程,可以这样理解,协程是轻量级的线程。
- Go协程的特点
有独立的栈空间
共享程序堆空间
调度有用户控制
协程是轻量级的线程
快速入门
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
"time"
)
func test() {
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
fmt.Println("test() hello world, world " + strconv.Itoa(i))
time.Sleep(time.Second)
}
}
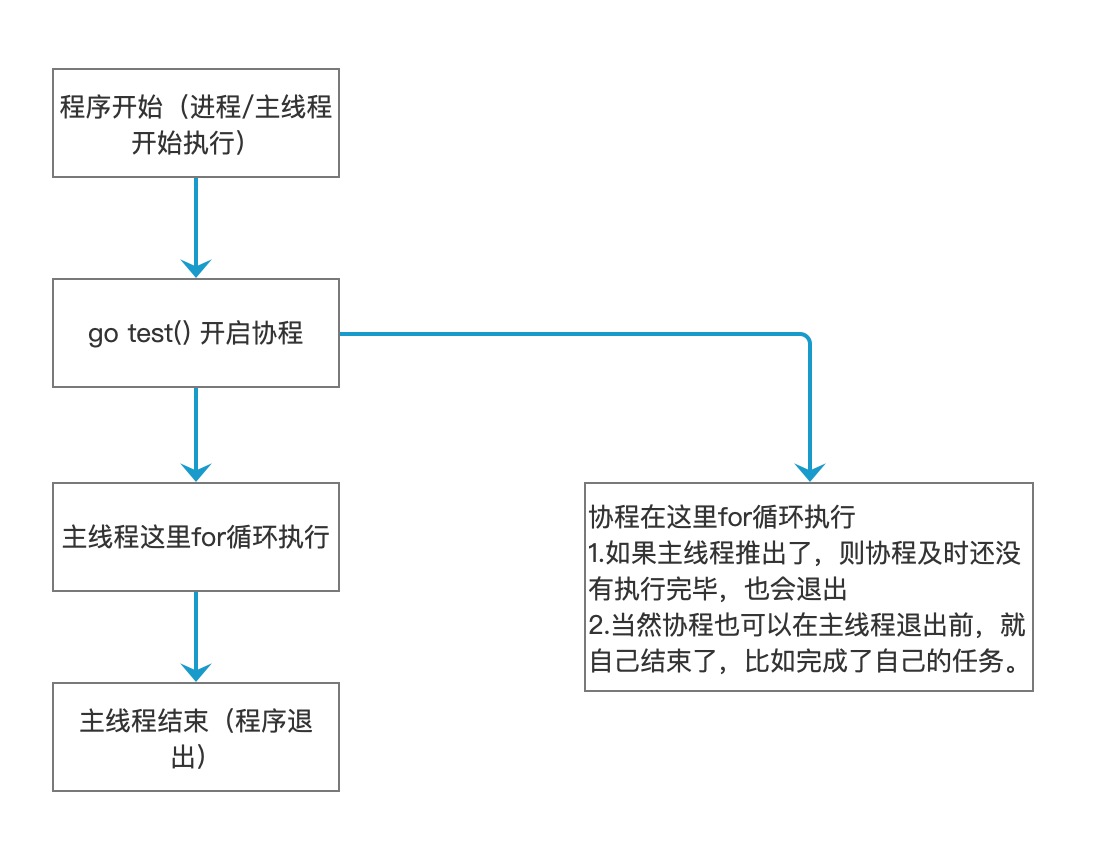
func main() {
go test() // 开启一个协程执行
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
fmt.Println("main() hello world, world " + strconv.Itoa(i))
time.Sleep(time.Second)
}
}
执行结果:
main() hello world, world 0 test() hello world, world 0 main() hello world, world 1 test() hello world, world 1 main() hello world, world 2 test() hello world, world 2 main() hello world, world 3 test() hello world, world 3 main() hello world, world 4 test() hello world, world 4 test() hello world, world 5 main() hello world, world 5 test() hello world, world 6 main() hello world, world 6 test() hello world, world 7 main() hello world, world 7 test() hello world, world 8 main() hello world, world 8 main() hello world, world 9 test() hello world, world 9
执行流程图:
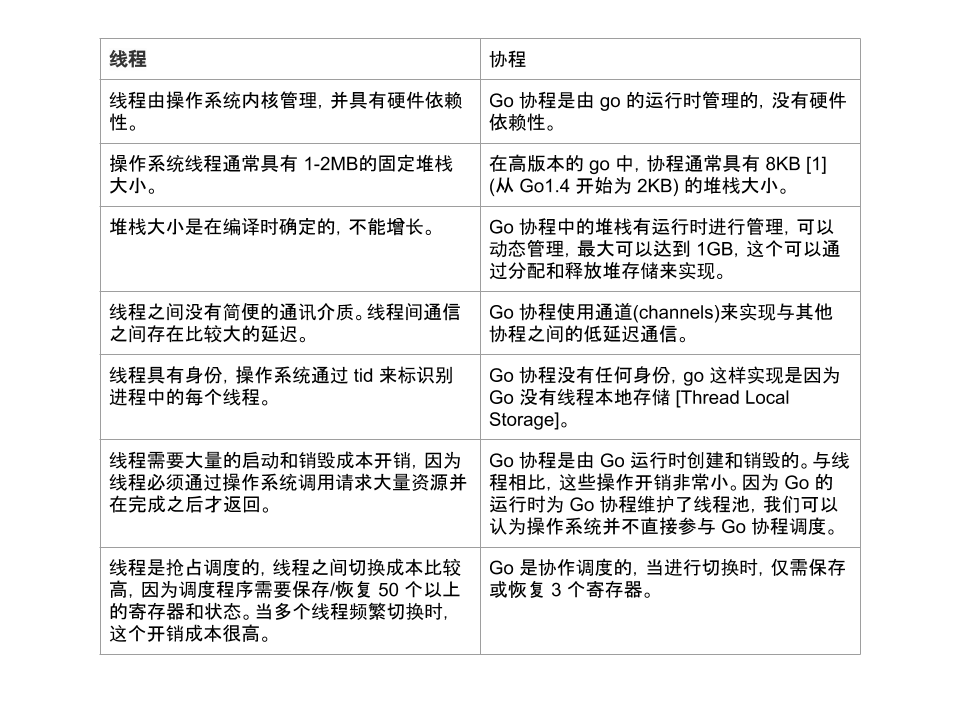
线程vs协程
小结
- 主线程是一个物理线程,直接作用在CPU上。是重量级的,非常消耗CPU资源。
- 协程从主线程开启的,是轻量级的线程,是逻辑状态,对资源消耗较小。
- Golang的协程机制是重要的特点,可以轻松的开启上万个协程。其他编程语言的并发机制一般是基于线程的,开启过多的线程,资源消耗较大,这了就凸显了Golang在并发上的优势了。